Delta Hedging: Mitigating Risk in Financial Markets
 In the fast-paced and unpredictable world of financial markets, investors and traders are constantly seeking strategies to minimize risk and maximize returns. One such technique that has gained popularity is delta hedging. Delta hedging is a risk management strategy employed by market participants to reduce or eliminate the exposure to price movements in an underlying asset. In this article, we will delve into the definition of delta hedging, explore different strategies, discuss its pros and cons, and conclude with its overall effectiveness as a risk management tool.
In the fast-paced and unpredictable world of financial markets, investors and traders are constantly seeking strategies to minimize risk and maximize returns. One such technique that has gained popularity is delta hedging. Delta hedging is a risk management strategy employed by market participants to reduce or eliminate the exposure to price movements in an underlying asset. In this article, we will delve into the definition of delta hedging, explore different strategies, discuss its pros and cons, and conclude with its overall effectiveness as a risk management tool.Definition:
Delta hedging is a method used to neutralize or offset the risk associated with the price fluctuations of an underlying asset. The “delta” represents the rate of change in the price of an option relative to changes in the price of the underlying asset. By dynamically adjusting the position in the underlying asset, investors can minimize or eliminate the impact of price movements on the value of their overall portfolio.
Strategies:
There are various strategies employed in delta hedging, depending on the specific needs and goals of the investor or trader. Some common strategies include:
- Delta-Neutral Strategy: This approach involves adjusting the position in the underlying asset to maintain a delta-neutral portfolio. It requires continuously monitoring and re balancing the portfolio to ensure the overall delta remains close to zero. By doing so, the investor aims to eliminate the risk of price movements in the underlying asset.
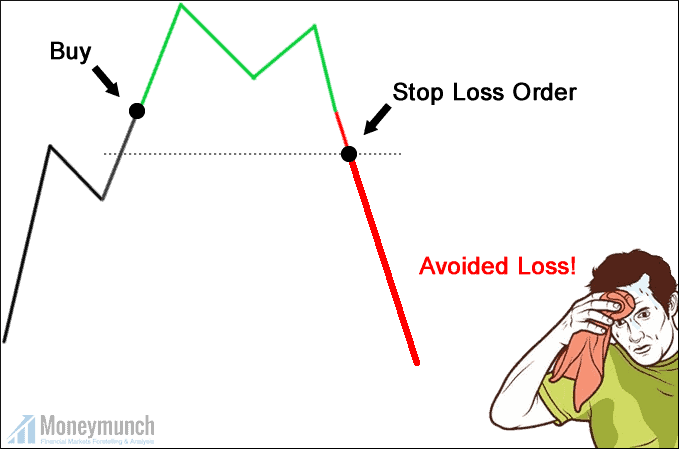
Stop-Loss: A Risk Management Tool for Traders
Strategies for High Probability Trades and Risk Management
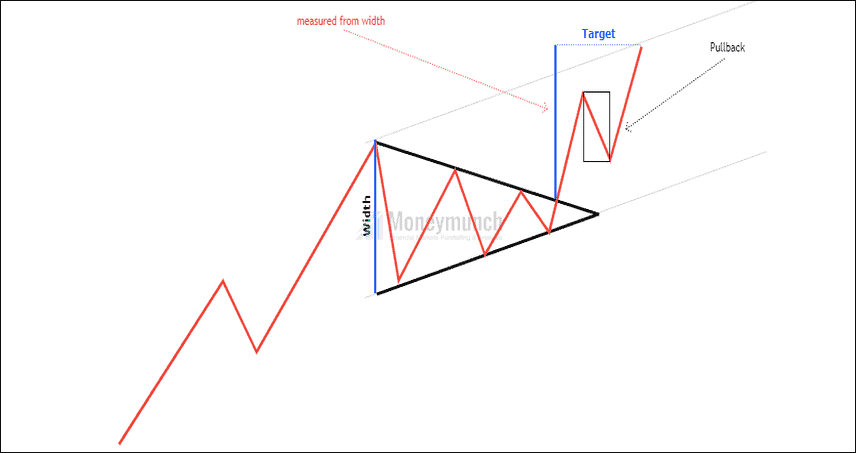
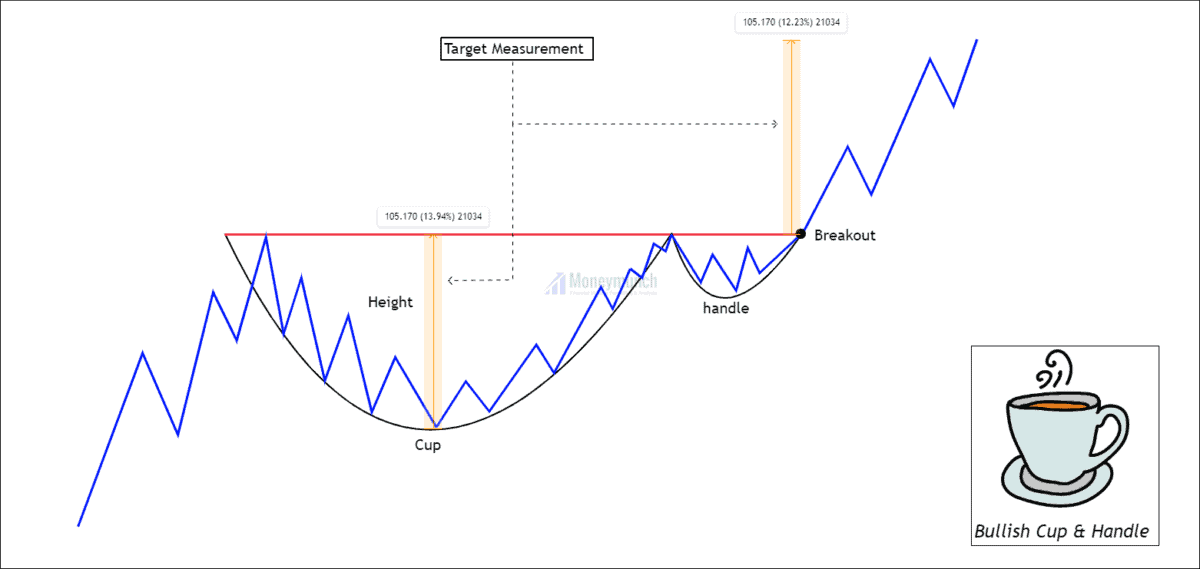
Bullish Cup and Handle Pattern
Type: bullish continuation
A cup and handle is a popular chart pattern among technicians. It had developed by William O’Neil and introduced in 1998. As the name suggests, the pattern is shaped like a cup with a handle. The shape of the cup is “U”, and the handle is pointing downward. The cup has a “U” shape and a downward-pointing handle. The ending point of the handle indicates buying opportunity. As soon as this part of the price formation is complete, the stock may reverse course and reach higher levels.
1. Prior trend: We are trading bullish continuation Cup & handle. So, the prior trend should be upward. It shows that the price will continue to trend after a retracement of the previous impulse. Buyers are generating demand to push the trend.
2. Construction: “U” shaped bottoms are an ideal pattern and more reliable than “V” bottoms because there is almost no consolidation in this case. The perfect pattern would have equal highs on both sides of the cup, but this does not often occur.
3. Duration: It is possible to spread the cup out over 1 to 6 months, and occasionally longer. The handle should form and finish over a period of 1-4 weeks.
4. Breakout: The pattern confirms a bullish trend when it breaks above the neckline formed by the previous highs with good volume. A buy point is reached when the stock breaks out or moves upward through the old resistance level (right side of the cup).
5. Volume: During the base of the bowl, the volume should decrease as prices decline, remaining lower than average; then, it should increase when the stock begins to move higher, back up to the previous high.
6. Timeframe:
- Cup and handle patterns can unfold over weeks or months.
- Adapt your trading strategy to your preferred time frame.
7. Profit targets: It is calculated based on the depth of the cup as a profit target. The breakout level can be determined by extending the distance from the bottom of the cup to the neckline and measuring upward from there.
8. Stop-loss: It is ideal to place the stop-loss at the bottom of the handle. Also, You can place the stop-loss below the swing low if the price oscillated within the handle several times.
Continue reading

 Lock
Lock